EXPERIMENT NO. 3
AIM
:- A study of the characteristics of a zener diode.APPARATUS :- Power supply, microammeter, voltmeter, millivoltmeter, rheostat, zener diode, connecting wires.
FORMULA:-
Dynamic resistance of zener diode, rz = (delta)Vz / (delta)Iz
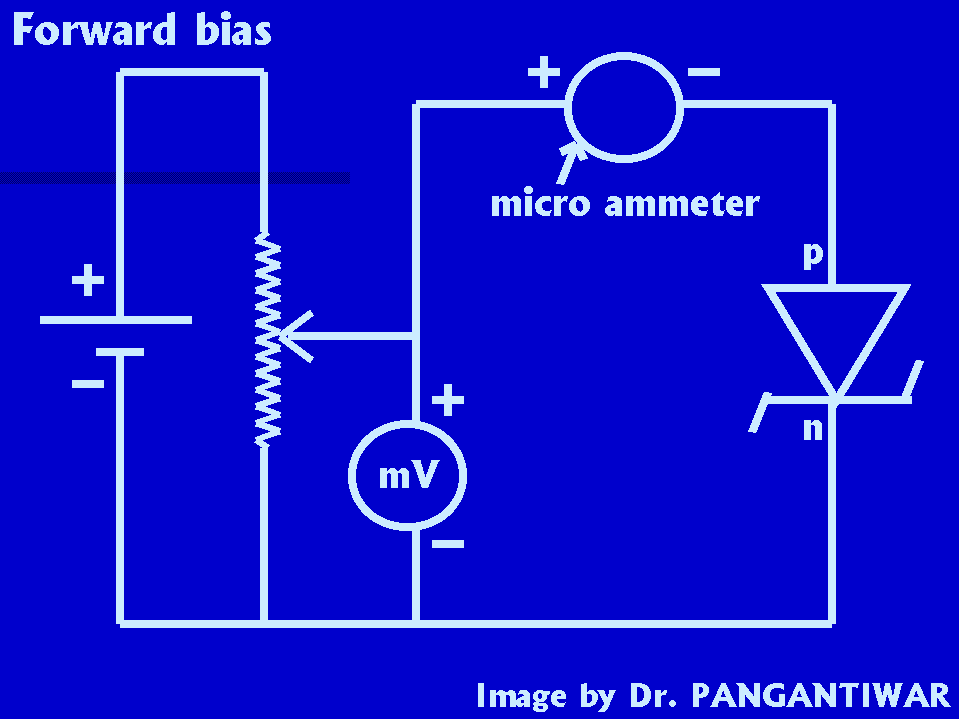
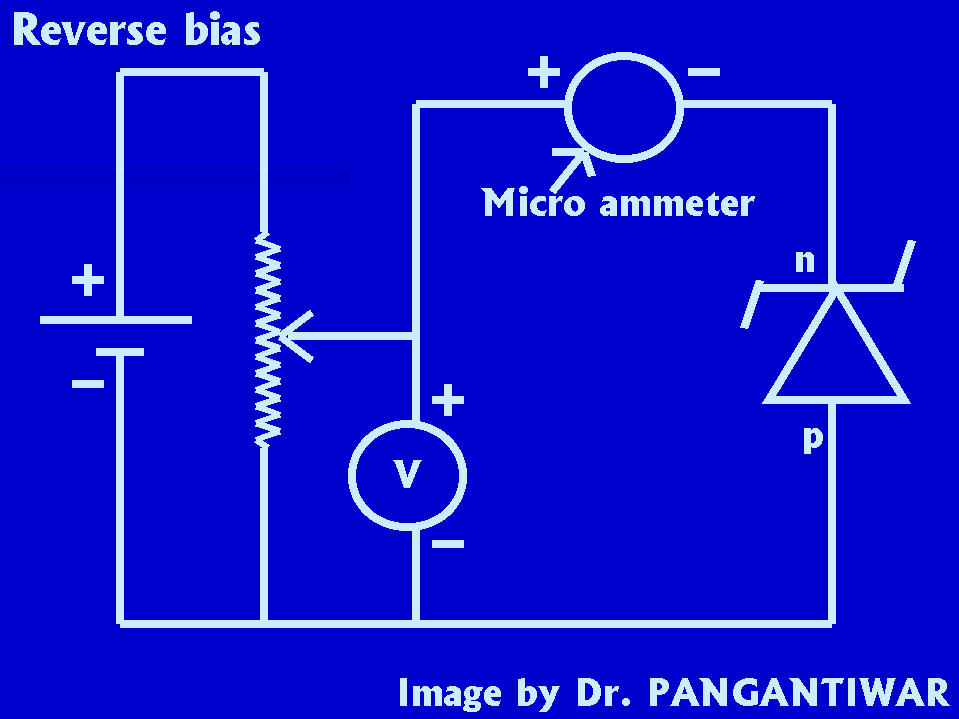
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:-


PROCEDURE:- Make the connections as shown in circuit diagram for forward bias. Switch on the power supply. The voltage is set at 0 V and the current through the zener diode shown by micro-ammeter is recorded. With the help of slider of rheostat, the voltage is increased in steps of 10 mV. For each setting of the voltage, corresponding current shown by the micro-ammeter is noted. The observatuions are recorded in table.
Then the connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram for reverse bias. The reverse voltage is set at 0 V and the current shown by the micro-ammeter is recorded. Then the voltage is increased in steps of 1 V till the current suddenly tend to rise. Now the voltage is increased in steps of 0.1 V and the current shown by the micro-ammeter is recorded. All these readings are recorded in table.
|
Forward bias |
Reverse bias |
||
|
Voltage (mV) |
Current (micro A) |
Voltage (V) |
Current (micro A) |
|
0 |
0 |
||
GRAPH:-
The graph is plotted, by taking forward voltage on the positive x axis and forward current on the positive y axis for forward bias for getting forward characteristics and by taking reverse voltage on the negative x axis and reverse current on the negative y axis for reverse bias for getting reverse characteristics, by selecting suitable scale for forward and reverse bias readings.
From the graph, the cut-in voltage, zener breakdown voltage and dynamic resistance in the zener region are calculated.
RESULT:-
i) Cut - in voltage =
ii) Zener breakdown voltage =
iii) Reverse dynamic resistance in zener region, rz =
PRECAUTIONS:-